Vector 动态数组容器¶
STL大道之始,若要透彻的去了解STL,没有比写一遍他更好的办法了
框架¶
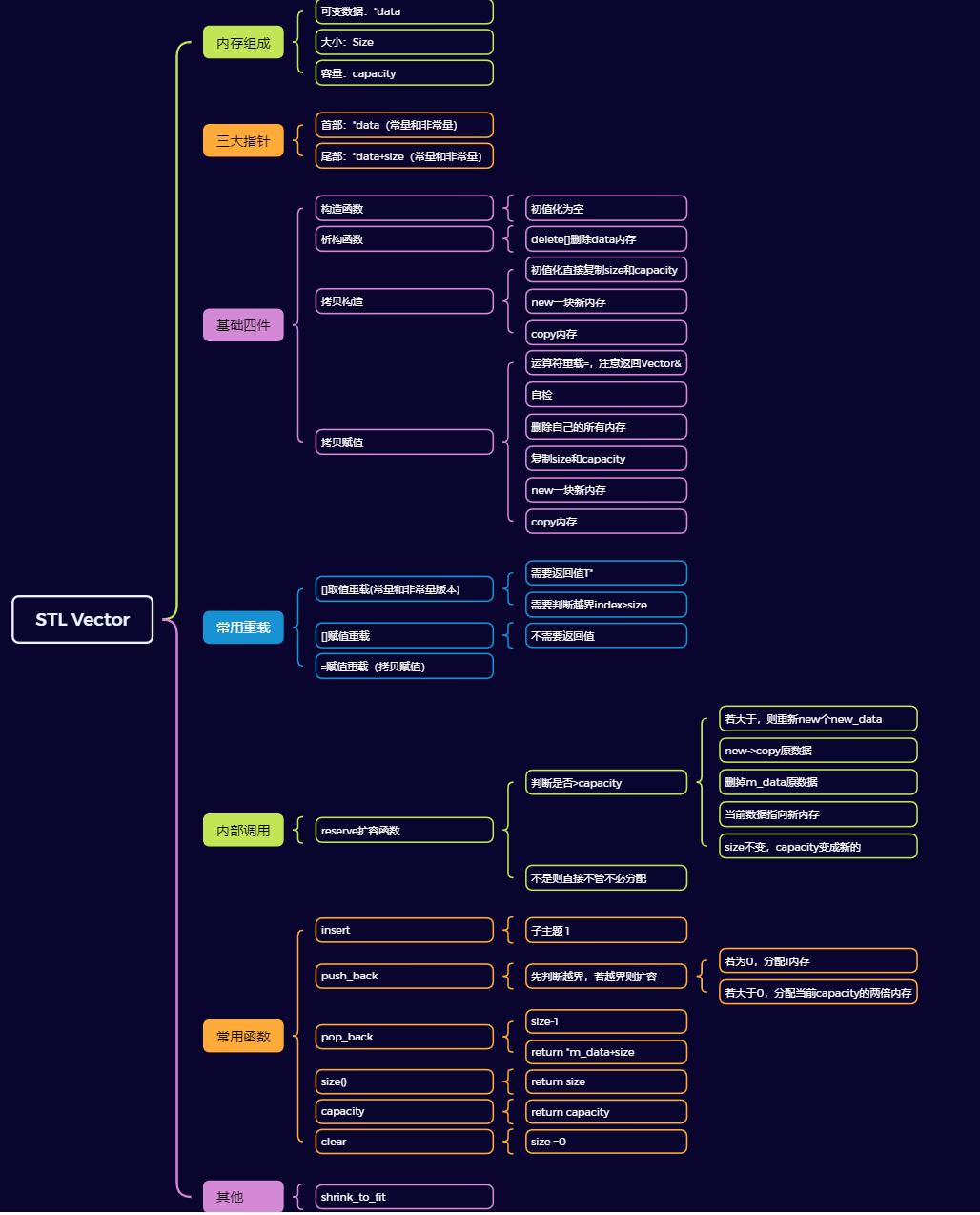
内存组成¶
分为数据、大小和容量
private:
T* m_data;
size_t m_capacity;
size_t m_size;
基础四件¶
任何类都需要考虑实现的构造函数,拷贝构造,拷贝赋值,析构
//----------------基础函数-----------------
//ctor
MyVector() :m_data(nullptr), m_capacity(0), m_size(0) {};
//dtor
~MyVector()
{
delete[] m_data;
}
//copy constructor 拷贝构造
MyVector(const MyVector& other) :m_capacity(other.m_capacity), m_size(other.m_size) //为什么可以访问私有变量呢?
{
m_data = new T[m_capacity];
std::copy(other.m_data, other.m_data + m_size, m_data); //移动数据
}
//Copy Assignment 拷贝赋值
MyVector& operator =(const MyVector& other)
{
//自检
if (this != &other)
{
delete[] m_data;
m_capacity = other.m_capacity;
m_size = other.m_size;
m_data = new T[m_capacity];
std::copy(other.m_data, other.m_data + m_size, m_data); //移动数据
}
return *this;
}
首尾指针¶
常常和迭代器搭配使用的首尾指针
T* begin()
{
return m_data;
}
T* end()
{
return m_data + m_size;
}
扩容函数¶
作为容量管理的基础,这里就简单的扩容两倍来简化STL
private:
//扩容函数
void reserve(size_t new_capacity)
{
//判断是否需要扩容
if (new_capacity > m_capacity)
{
T* new_data = new T[new_capacity];
std::copy(m_data, m_data + m_size, new_data);
delete[] m_data;
m_data = new_data;
m_capacity = new_capacity;
}
}
运算符重载¶
除了之前的拷贝赋值外,这里还对【】下标取值作了重载
//public MyVector<T> operator[](const int& index)
//注意,这是数组取值,返回的是一个值
T& operator[](size_t index)
{
//先判断index是否越界
if (index >= m_size)
{
throw std::out_of_range("index out of range");
}
return m_data[index];
}
//const 版本的访问
const T& operator[](size_t index) const
{
if (index >= m_size)
{
throw std::out_of_range("index out of range");
}
return m_data[index];
}
常用函数¶
剩下的就是Vector常用的一些方法函数
void push_back(const T& value)
{
//先判断容量是否够用
if (m_size == m_capacity)
{
//先申请空间
reserve(m_capacity == 0 ? 1 : m_capacity << 1);
}
//插入数据
m_data[m_size++] = value;
}
int size()
{
return m_size;
}
int capacity()
{
return m_capacity;
}
T insert(size_t index, T value)
{
//先判断index是否越界
if (index > m_size)
{
throw std::out_of_range("index out of range");
}
if (index == m_size)
{
reserve(m_capacity == 0 ? 1 : m_capacity << 1);
}
//移动数据
for (size_t i = m_size; i > index; i--)
{
m_data[i] = m_data[i - 1];
}
m_data[index] = value;
++m_size;
}
void pop_back()
{
if (m_size > 0)
{
--m_size;
}
}
void clear()
{
m_size = 0;
}
补充¶
除了前面仿写的一些主要功能,还有一些Vector特性没有描述出来。下面是C11之前的一些函数用法: * assign * get_allocator * at * data * 逆向迭代器 * cbegin、cend、rbegin、rend系列(C11) * empty * max_size * reverse 重分配 * emplace(C11) * erase * empalce_back(c11) * swap * operator == * shrink_to_fit 返回多余内存
分配器和迭代器¶
自动分配和迭代的实现,这里就没写了。 总之用的是随机访问迭代器
Vector<bool >节省空间的动态 bitset (类模板特化)¶
其中元素并不是bool类型而是bit,通过位数上的01有效节省开销。
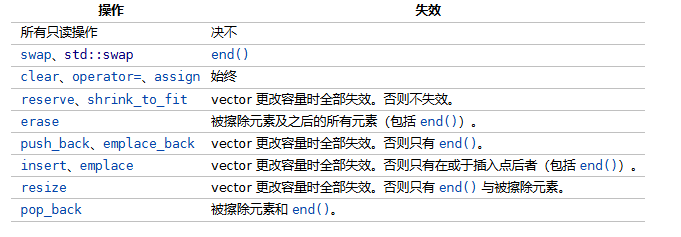
迭代器失效¶
一些对数据的操作常常会引发迭代器失效问题,如果我们再使用迭代器就会产生不正常的问题。